RFID Basics: What It Is & Why It Matters
Understand the fundamentals of RFID technology and why it’s revolutionizing DoD inventory management.
How RFID Works
A Typical UHF RFID System
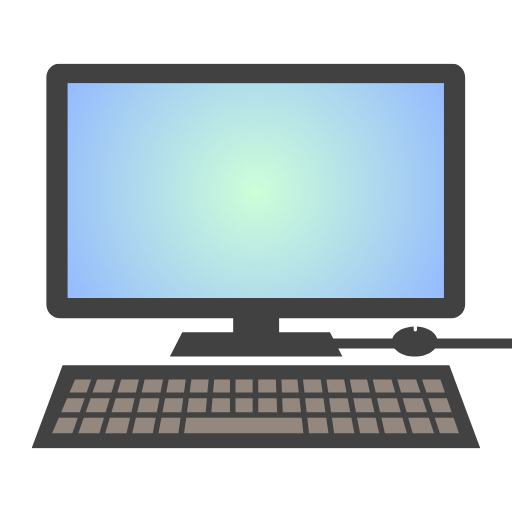

Inventory Computer
Controls all RFID readers in system and keeps track of all items in inventory in real time.
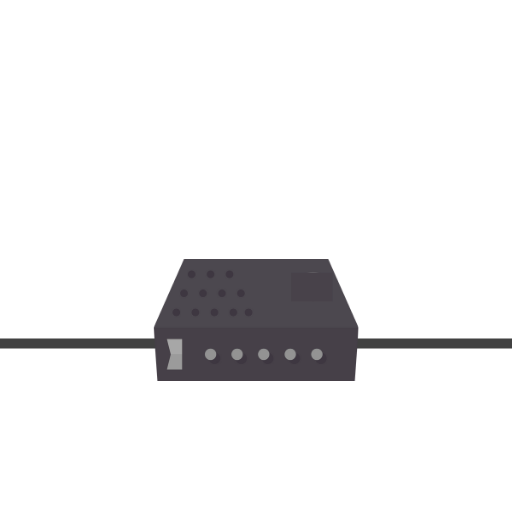
RFID Reader
Sends and receives RF signals from antenna and extracts RFID tag numbers.

Antenna
Radiates and receives RF energy over a specified coverage area.
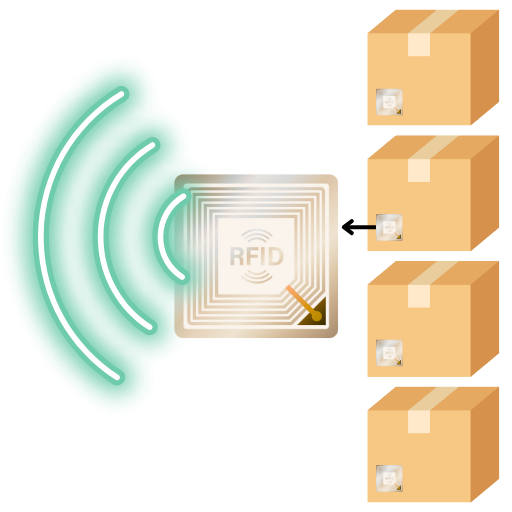
RFID Tag
Reflects the transmitted signal with a coded modulation unique to the tag. Powered by transmitted RF energy.
- A single inventory computer may control many RFID readers simultaneously.
- Each reader may control up to four antennas independently.
- A very large number of RFID tags may be read simultaneously by one reader.
Key RFID Benefits
Reads 700–1000 Tags/Sec
Process inventory faster than ever
100% Accuracy
Eliminate human error from manual counts
No Line-of-Sight Needed
Tags read through boxes, racks, and more
RFID vs. Barcode Technology
| Feature | RFID | Barcode |
|---|---|---|
| Line of Sight | ❌ Not Required | ✅ Required |
| Read Rate | 🔄 700–1000 tags/sec | 🐌 One at a time |
| Accuracy | ✅ Near 100% | ⚠️ Prone to human error |
| Inventory Time | ⏱ 95% faster | 🕓 Time-consuming |
| Automation Ready | ✅ Fully Automated | ❌ Manual Scanning Needed |
Choose the Right Solution for Your Operation
From high-volume warehouses to remote field deployments, our RFID systems deliver unmatched accuracy, speed, and reliability.
